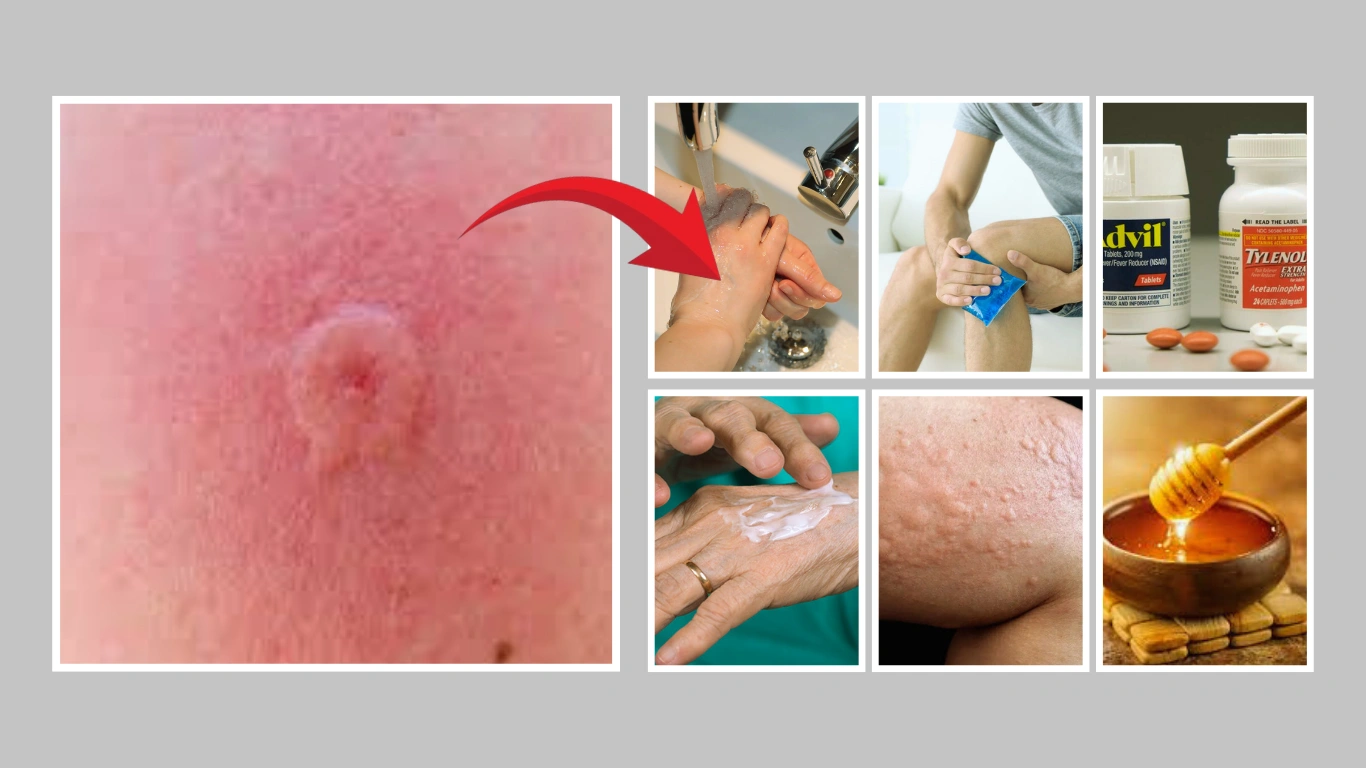
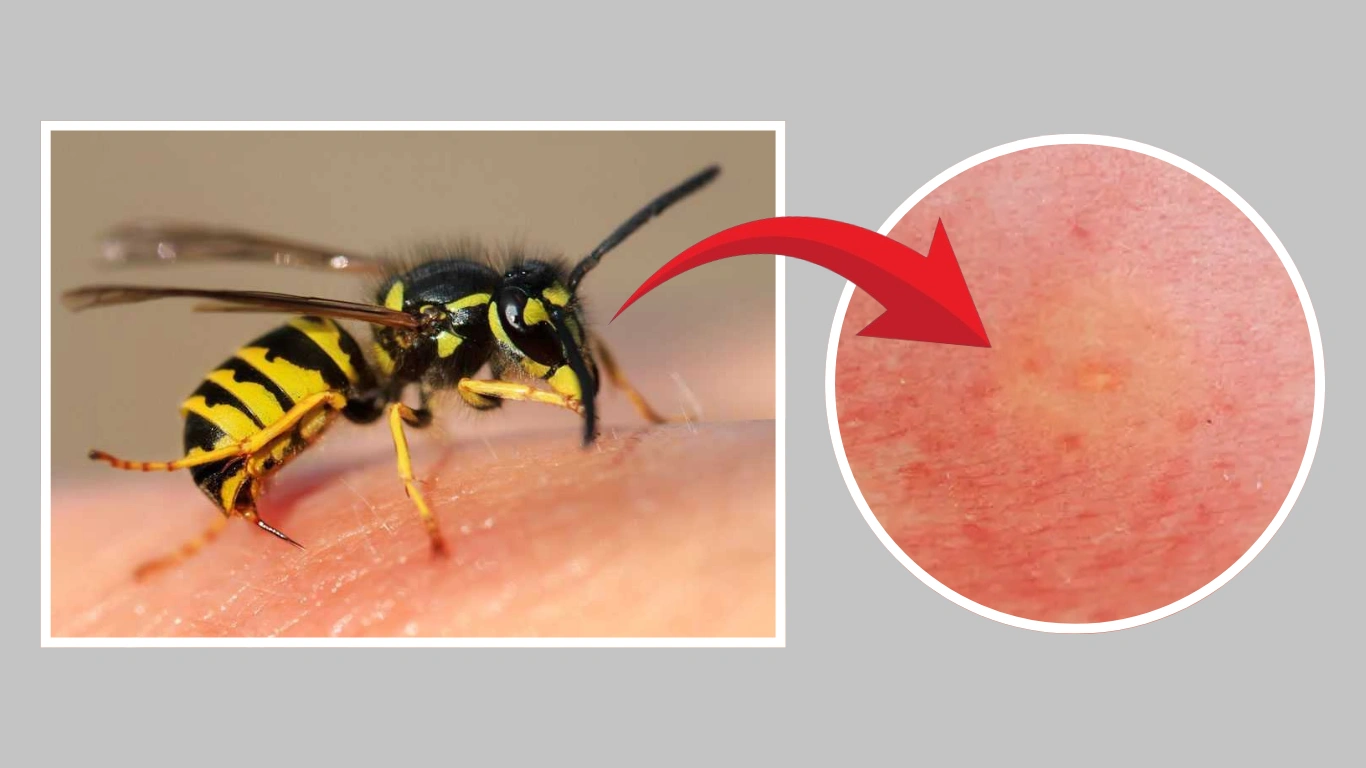
Getting stung by a wasp can be a painful and alarming experience, especially if you’re caught off guard. The sting usually causes swelling, redness, and a burning sensation—but with the right steps, you can ease the discomfort quickly. In this guide, I’ll walk you through seven effective methods to treat a wasp sting safely and naturally.
1. Clean the Area Thoroughly
Why It Matters
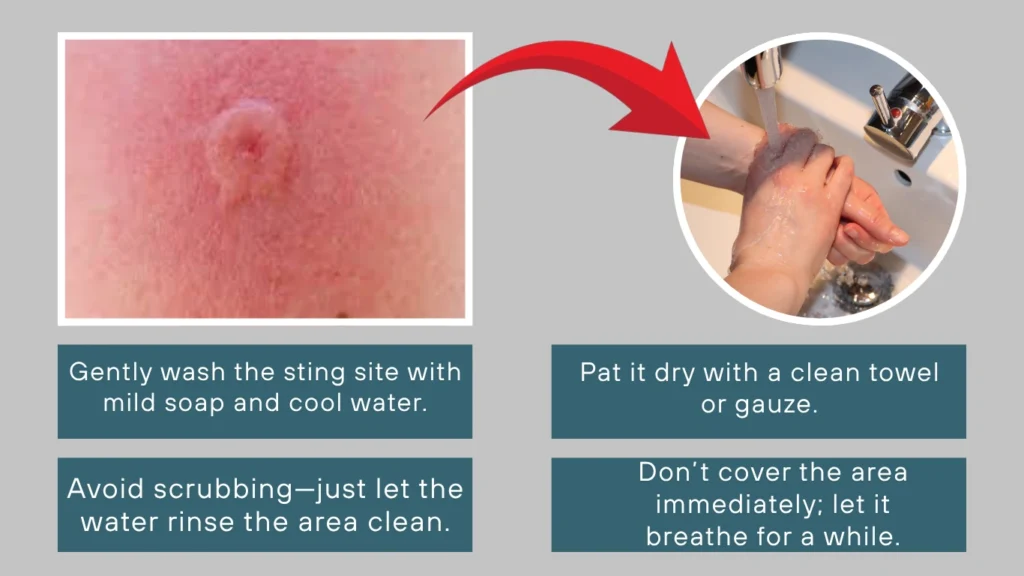
The first step after a wasp sting is to clean the affected area. This helps remove any venom residue, dirt, or bacteria, lowering the risk of infection. Skipping this step might lead to complications like swelling or delayed healing.
How to Do It
- Gently wash the sting site with mild soap and cool water.
- Avoid scrubbing—just let the water rinse the area clean.
- Pat it dry with a clean towel or gauze.
- Don’t cover the area immediately; let it breathe for a while.
2. Apply a Cold Compress
Benefits of Cold Therapy
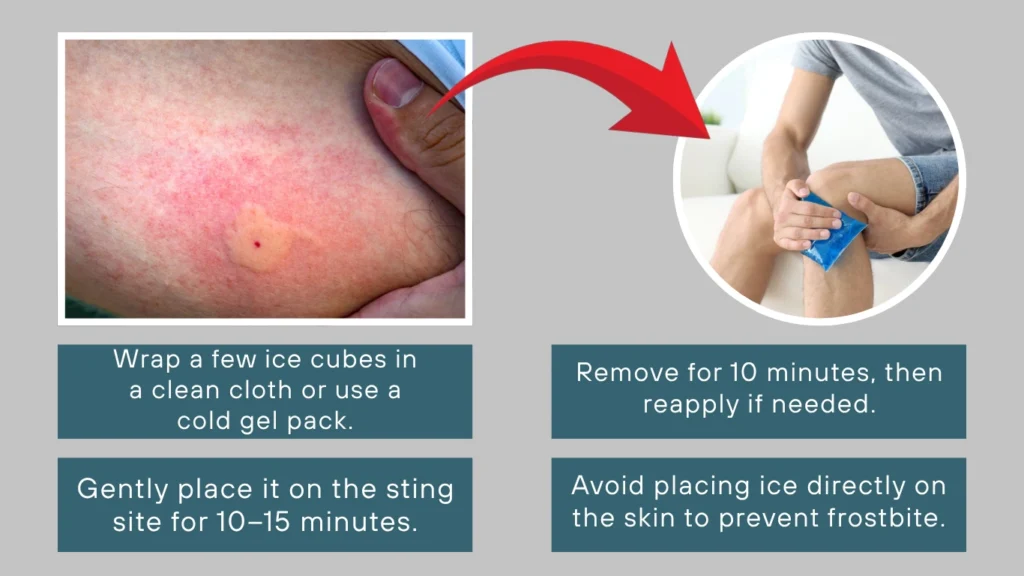
Applying something cold to the sting site helps reduce swelling, numb the pain, and slow down the spread of venom. This method is especially helpful in the first 30 minutes after the sting.
How to Apply
- Wrap a few ice cubes in a clean cloth or use a cold gel pack.
- Gently place it on the sting site for 10–15 minutes.
- Remove for 10 minutes, then reapply if needed.
- Avoid placing ice directly on the skin to prevent frostbite.
This method can bring quick relief and is one of the most accessible treatments for wasp stings.
3. Use Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
Recommended Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can ease both the pain and the allergic reaction caused by a wasp sting. Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen help reduce discomfort. Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can minimize swelling and itching.
Dosage and Caution
- Always follow the dosage instructions on the label.
- If you’re unsure, consult a pharmacist or healthcare provider.
- Avoid giving aspirin to children due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
- If symptoms worsen after taking medication, seek medical advice.
4. Apply Topical Treatments
Options You Can Use
You can reduce itching and inflammation by using creams or home remedies such as:
- Hydrocortisone cream (1%)
- Calamine lotion
- Baking soda paste (made by mixing with water)
- Antihistamine creams
How to Apply
- Clean and dry the sting site first.
- Gently apply a thin layer of your chosen cream or paste.
- Reapply as directed on the product label or every few hours for comfort.
- Avoid scratching the area, even if it feels itchy.
5. Elevate the Affected Area

When and Why to Do This
If the wasp sting is on your hand, foot, leg, or arm, elevating the area can help minimize swelling and reduce throbbing. Gravity helps drain excess fluid away from the sting site, leading to faster recovery and less discomfort.
How to Elevate Properly
- Rest the affected limb on a pillow above heart level.
- Keep it elevated for 15–30 minutes at a time.
- Repeat throughout the day, especially if swelling increases.
6. Monitor for Allergic Reactions
Warning Signs
While most wasp stings are mild, some people may experience serious allergic reactions. Keep an eye out for symptoms like:
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nausea or vomiting
What to Do If It Happens
- If symptoms appear, seek emergency medical help immediately.
- Use an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) if one is available and prescribed.
- Do not wait to see if symptoms get worse—act quickly, as allergic reactions can escalate fast.
7. Try Natural Remedies (Optional but Helpful)
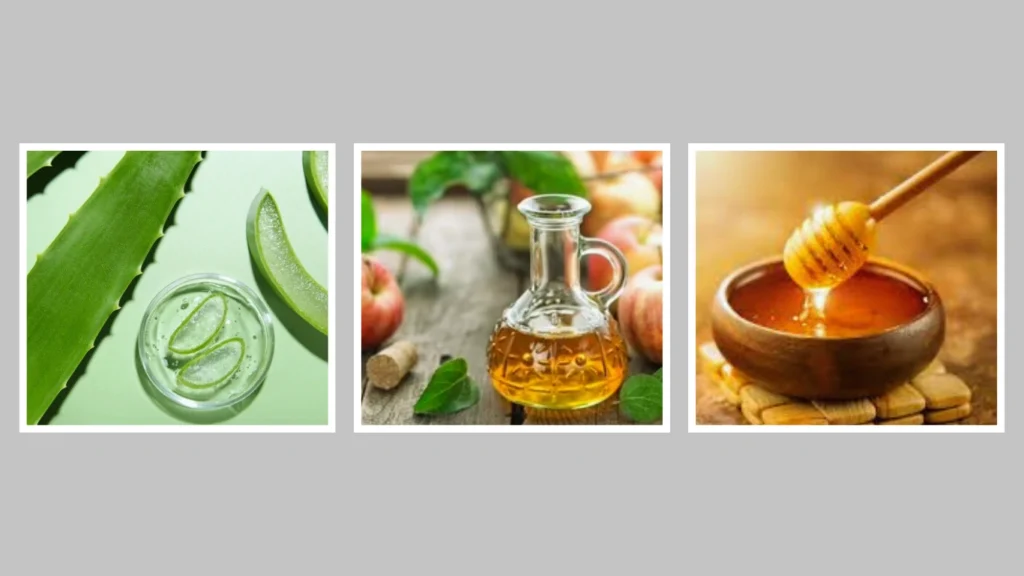

Common Remedies
Some natural treatments can provide additional relief if symptoms are mild and you’re looking for home-based care:
- Aloe Vera Gel – Soothes and cools the sting site.
- Apple Cider Vinegar – May help neutralize venom and reduce itching.
- Honey – Has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
How to Use Safely
- Always do a patch test first to avoid further irritation.
- Apply a small amount directly to the cleaned sting area.
- Leave it on for 15–20 minutes before rinsing off.
- Use these remedies only when no signs of allergic reaction are present.
When to See a Doctor
Why Medical Attention Might Be Necessary
Most wasp stings are harmless and heal within a few days. However, there are situations where medical attention becomes crucial to avoid serious complications. Knowing when to call a doctor can help prevent infections or allergic emergencies.
Seek medical help if you notice:
- Increasing Swelling or Redness: If the area continues to swell after 48 hours or spreads significantly.
- Signs of Infection: Pus, warmth, red streaks extending from the sting site, or a fever may indicate infection.
- Persistent Pain: If pain doesn’t ease after using over-the-counter medication or home remedies.
- Stings Near the Face or Throat: Swelling in these areas can interfere with breathing or vision.
- Multiple Stings: Especially in children, older adults, or if stung many times at once.
- Unusual Reactions: If you feel confused, faint, or notice anything out of the ordinary after a sting.
Don’t hesitate to seek emergency help if you suspect a severe allergic reaction. It’s always better to act early than to wait and risk complications.
Final Thoughts
Wasp stings are painful, but with the right care, most people recover quickly and without complications. The key is to act fast—clean the area, reduce swelling, and watch for any unusual symptoms. Whether you prefer over-the-counter products or natural remedies, the goal is the same: comfort and healing.
FAQs
How long does a wasp sting take to heal?
Most wasp stings heal within 1 to 3 days. Mild swelling and redness may last a bit longer, but with proper care, symptoms usually improve quickly. If swelling persists after 3 days, it’s best to consult a doctor.
Can I be allergic to a wasp sting even if I’ve never had a reaction before?
Yes. Allergic reactions can develop unexpectedly, even if previous stings caused only mild symptoms. Always monitor your body after a sting, especially if it’s your first time.
Is baking soda or vinegar better for a wasp sting?
Both can help, but baking soda is often preferred to neutralize the acidic venom and soothe itching. Vinegar is more commonly used for jellyfish stings but may help some people with wasp stings too.
What should I do if I get stung multiple times?
Clean all sting sites, apply a cold compress, and take an antihistamine to control swelling. If you experience dizziness, trouble breathing, or widespread swelling, seek emergency care immediately.
Can children be treated the same way as adults?
Generally, yes—but with more caution. Use child-appropriate dosages for medications, and keep a close watch for any signs of allergic reaction. When in doubt, consult a pediatrician.